


A missed period is often the most important early symptom of pregnancy. However, often a woman may experience many other non-specific symptoms even before missing the menses. The most common ones reported are: breast and nipple enlargement with tenderness, constipation, bloating, fatigue, exhaustion, nausea and vomiting (although more commonly it occurs later), increased sensitivity to odors, abdominal cramping or pain, headaches and backaches, spotting (due to implantation bleeding), mood swings and aversion to certain foods or beverages. It is important to note that it is not necessary that all pregnant women will have all these symptoms. They vary from person to person, and in many cases may be totally absent. Furthermore, many of these overlap with PMS (Premenstrual Syndrome), thus are non-specific for pregnancy.
Whenever a pregnancy is suspected, it is confirmed or ruled out either by a urine test or a blood test. Tests for pregnancy are often done for the first time before the expected menses or after missing the period. All these tests are based on detection of the hormone hCG (Human Chorionic Gonadotropin) or its metabolites in either urine or blood. The blood test for hCG or its products is more accurate and can detect much lower levels of hCG as compared to the urine test. Some of the most sensitive blood tests for hCG can detect it as early as one week after conception.
A false-negative serum hCG test (i.e. pregnancy test is negative, but the woman is pregnant) is quite common if the test is done too early. Often many women undergo the pregnancy test even before missing the menses. The hCG test can be false negative in this scenario. However, as the time passes, the likelihood of a negative test being a false-negative is greatly reduced. A negative serum hCG test few days after the expected date of menses is extremely unlikely to be false-negative. Note carefully, that we are talking here of serum hCG test and not the urine test. Urine test has lower sensitivity and has much higher chances of being false-negative even after missing the menses.
Another important cause of false-negative test could be variations in the time of ovulation. This may occur even if a woman has regular menstrual cycles. A late ovulation may occur in some women, and this may delay the detection of hCG in the serum. The hCG in serum can be detected as early as 8 days after ovulation, although sometimes it may take up to 2 weeks to be detectable, depending upon how much time it takes for the implantation to occur after conception.
False-negative results on a blood pregnancy test may also result due to a 'high-dose hook effect'. In this, the test becomes negative because of very high concentration of hCG. This may occur especially in molar pregnancy, although more common finding is a falsely low value of hCG rather than a completely negative test. This occurs when high level of hCG overwhelms the assay used to detect it. Diluting the serum often gives the correct results and overcomes this hook effect. However, this is an extremely rare possibility with only a few cases described.
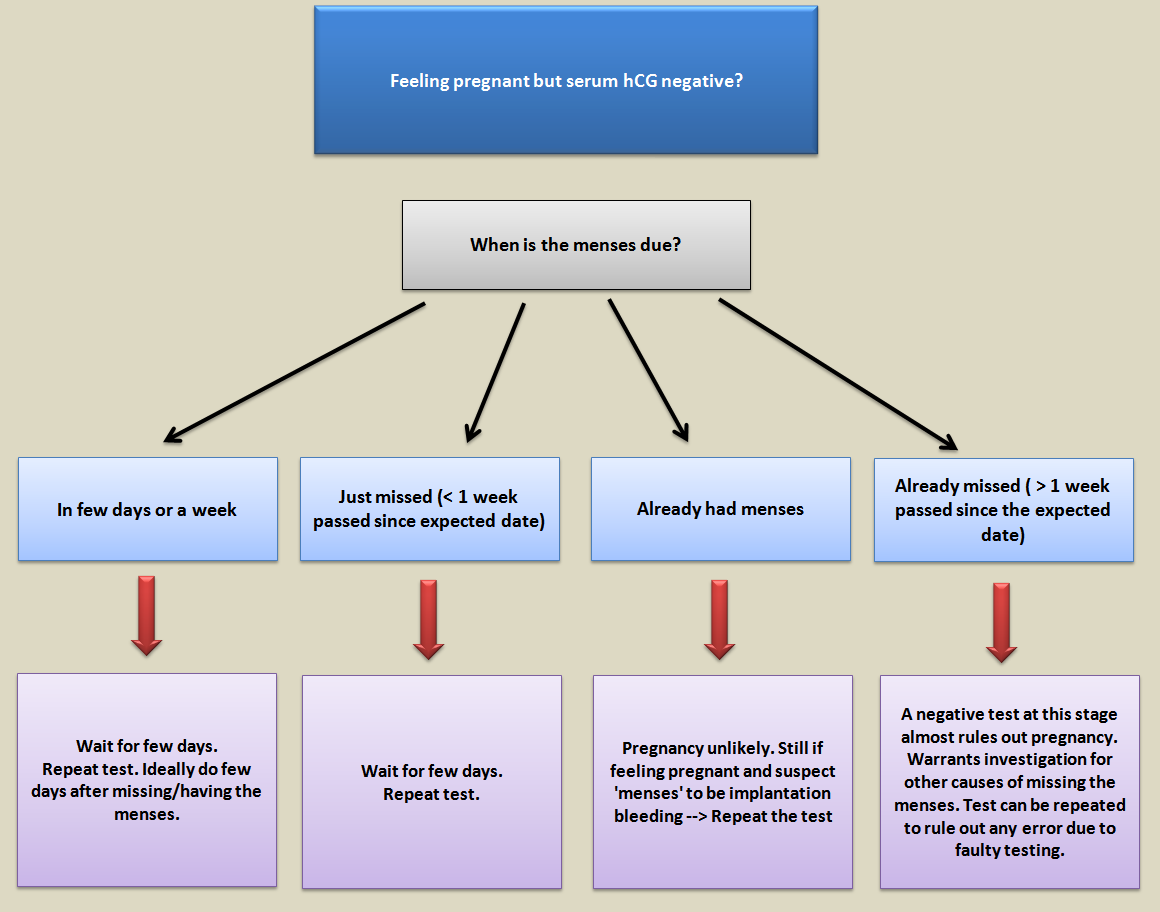
So what should be done if your blood test is negative and still you feel you are pregnant? The answer to this question depends on whether your expected date of menses has passed or not. If you are still awaiting your menses, there is a fair chance that the test could be false negative. Best thing is to repeat the test after few days, ideally after missing/having the menses. If you missed your menses just few days ago and the test is negative, take a repeat test after 2-3 days. If you had your menses but still feel pregnant, it would be wise to get a repeat test a couple of days after the menses to be sure that you are not pregnant and the perceived 'menses' was not an implantation bleeding. A negative test one week after missing the menses may warrant investigation for other causes of missed menses. The test can be repeated one more time, to rule out the possibility of false negative due to faulty testing (although this is uncommon). You may still feel pregnant even after this repeat test, but it is almost certain that you are not. The symptoms resulting in 'feeling' pregnant may be due to some other cause(s) and you may need to consult your doctor for this. You may also feel so if you are trying very hard to get pregnant, and find it hard to accept a negative test.