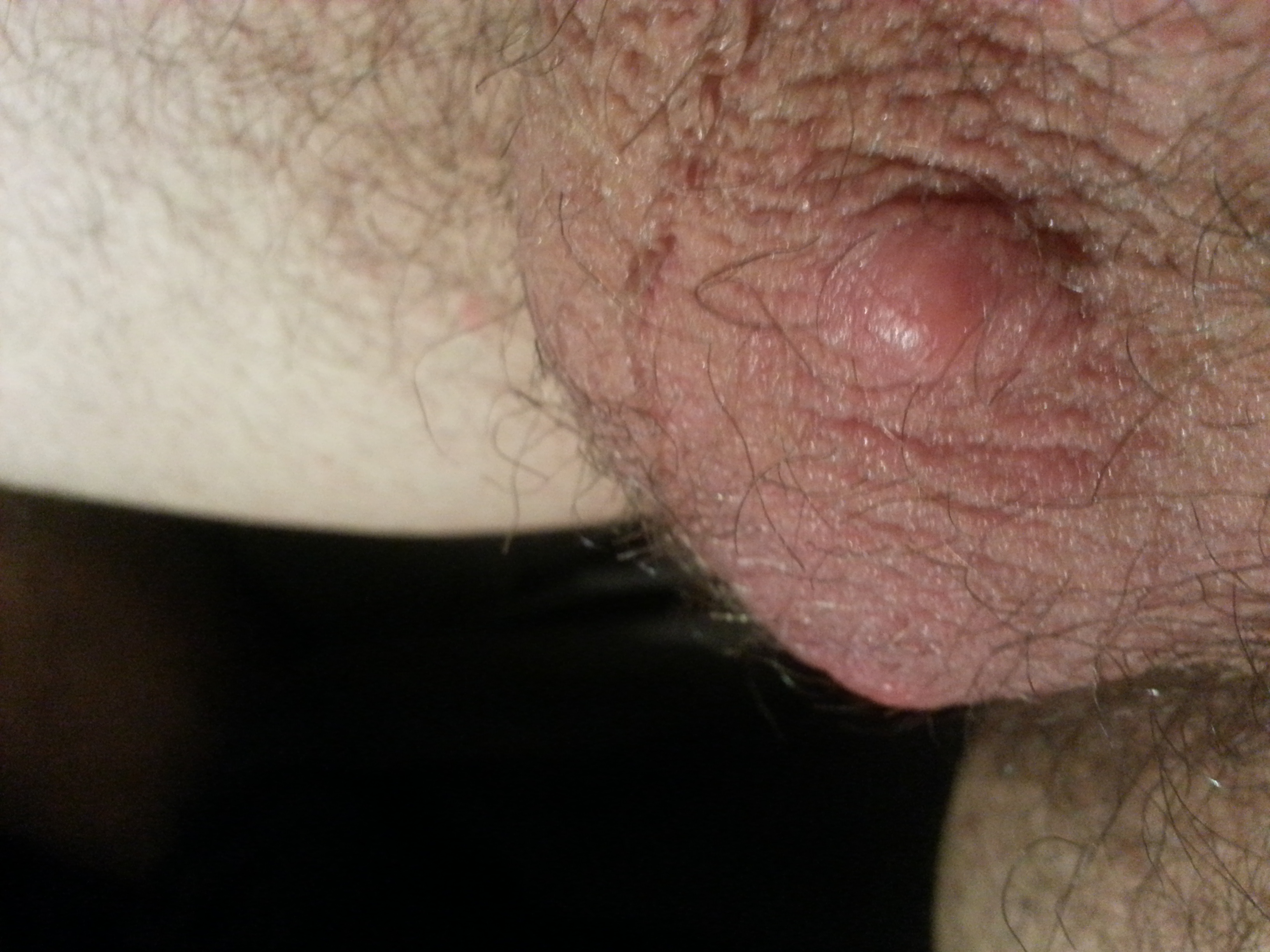
 The scrotum is basically a pouch of skin that hangs behind the penis and contains the testicles. These testicles produce testosterone and sperm (semen). A lump in the scrotum is often a cause of concern for men and boys. The lump can be cancerous, but it may also be caused by other less serious conditions. Usually, having a lump in scrotumrequires a quick visit to your doctor, even if it is painless and you don't have other symptoms.
The scrotum is basically a pouch of skin that hangs behind the penis and contains the testicles. These testicles produce testosterone and sperm (semen). A lump in the scrotum is often a cause of concern for men and boys. The lump can be cancerous, but it may also be caused by other less serious conditions. Usually, having a lump in scrotumrequires a quick visit to your doctor, even if it is painless and you don't have other symptoms.
What Are the Symptoms of Lump in Scrotum?
The symptoms of lump in scrotum may vary from person to person and usually depend on what causes a lump in the first place. Sometimes, you may not experience any symptoms at all other than a small mass in your scrotum that you can feel with your fingers. On other occasions, you may experience a sudden pain, a dull ache, or a feeling of heaviness in your scrotum. Other common symptoms include:
- Hard or swollen testicles
- Pain that travels to your abdomen, groin and back
- A red, swollen scrotum
- Fever with frequent urination
- Blood or pus in urine
- Nausea or vomiting
- A swollen epididymis which is the tube located right behind your testes and transports sperm
Whatever the symptoms are, you should go see your doctor, and seek immediate medical attention if the lump is painful.
What Causes Lump in Scrotum?
You may feel a lump on testiclesfor so many reasons. It could be benign or malignant, but it usually happens due to one of the following causes:
1. Benign Causes
- Hydrocele. The sac that surrounds testicles has several layers around it, but in some cases, excess fluid accumulates between the layers, causing a painless swelling of the scrotum.
- Hematocele. When the layers of a sac that houses each testicle are filled with blood, this may cause swelling of the scrotum. This usually results from a direct blow to the testicles or due to other traumatic injuries.
- Spermatocele. Also known as an epididymal cyst or spermatic cyst, spermatocele is a condition that leads to the development of fluid-filled sac in the scrotum. This noncancerous, painless cyst usually develops above the testicle.
- Varicocele. The condition refers to the enlargement of the veins within your scrotum that transport oxygen-depleted blood from epididymis and testicles. The lump may appear on the left side of the scrotum more often which is mainly due to the differences in how blood circulates from different sides. It may be painless, but it can cause infertility.
2. Malignant Causes
- Inguinal hernia. In this condition, a portion of your small intestine puts pressure on the tissues, separating the groin and abdomen. Sometimes, it pushes through a weak spot in the tissue and appears as a mass or lump in the scrotum. It is usually quite common in infants when the passageway from the abdomen to the scrotum doesn't close during development.
- Orchitis. A viral infection, known as mumps, is usually the root cause of this malignant condition that leads to the inflammation of the testicle. Sometimes, the condition is caused by a bacterial infection that also infects the epididymis.
- Epididymitis. The comma-shaped structure behind your testicle may get inflamed due to a bacterial infection. The condition is called epididymitis and is often caused by Chlamydia or other sexually transmitted bacterial infections. An abnormal flow of urine or a viral infection may also lead to epididymitis.
- Testicular torsion. This condition refers to the twisting of the blood vessels, the spermatic cord, nerves and the tube that takes semen to the penis. This can be an extremely painful condition because the blood supply to the testicle is cut off, and if not treated promptly, it may even result in permanent damage to the testicle. The affected testicle might seem enlarged or higher than normal.
- Testicular cancer. The lump in scrotummay well be a tumor that contains abnormal testicular tissue. You can feel this cancerous growth with fingers. The tumors may not cause any symptoms whatsoever, but some men may experience painful swelling.
How Is Lump in Scrotum Treated?
You don't need a treatment in most cases, but you may need moreserious procedures to deal with cancerous lumps. Here is a bit more about the treatment options for a lump in scrotum:
1. Benign Lumps
Benign lumps are usually painless and don't affect your health a lot. You can leave it untreated or have it repaired, drained or removed surgically.
2. Infections
You may have to take antibiotics when the lump in scrotum is the result of a bacterial infection. Viral infections causing orchitis or epididymitis are treated with ice, rest and pain relief medication.
3. Testicular Cancer
The treatment for testicular cancer is usually quite complex. Only an oncologist can help you treat a cancerous lump in your scrotum. The cancer specialist will check if the cancer is limited to a testicle or has already spread to other tissues in your body. Your age and medical history will also have an impact on what treatment option works best for you. The treatment may include the following options:
- Radical inguinal orchiectomy. Known as the primary treatment for a cancerous lump on testicle, it involves removing the affected testicle as well as the spermatic cord. It's a surgical procedure and your doctor will remove your testicle through an incision in the groin. Sometimes, the surgeon has to remove the lymph nodes in your abdomen if the cancer has spread to them.
- Radiation therapy. This treatment option requires undergoing a therapy in which your doctor will use high-dose x-rays to destroy cancer cells. A radiation therapy is usually the treatment choice after the surgeon has already removed the testicle and wanted to eliminate the remains of cancer cells in the scrotum.
- Chemotherapy. Sometimes, your cancer specialist may opt for a drug treatment to kill cancer cells. This drug treatment involves making use of powerful chemicals that exterminate cancer cells.
You will improve your chances of getting rid of a cancerous lump if you start your treatment early. Therefore, it is important to have a regularcheck to ensure there is nosign of testicular cancer.


