


Throat cancer can originate in any region of the throat, including the pharynx, larynx, and tonsils. All of these areas are difficult to operate on without affecting the patient's face or ability to talk. In order to avoid lengthy surgery and lower the severity of treatment, you should be aware of the warning signs of throat cancer. This will help you detect a problem earlier to facilitate treatment.
Throat cancer symptoms depend on where the cancer originated and what type of growth it is. A doctor will help you to determine what type of cancer you have and what stage of development it is in. It is important to be aware of what to look for so that you can determine whether or not you have a problem requiring medical attention.
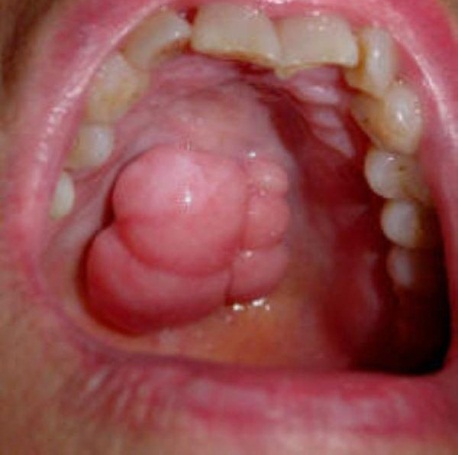
1. Lumps and sores. Sores throughout the mouth and throat are the most common throat cancer symptoms. They will commonly start out small, looking similar to a canker sore or similar irritation, but can quickly develop into a large, intrusive lump. Sores will be large and flesh colored, or very dark, depending on the type of cancer. The most common spots for sores to develop are on the roof of the mouth, the back of the throat, or under the tongue. Most mouth irritations or diseases lead to the development of sores, so it is important to watch these carefully to determine if they are a serious threat. Sores that do not appear to heal, or seem to rapidly increase in size, may be cancerous.
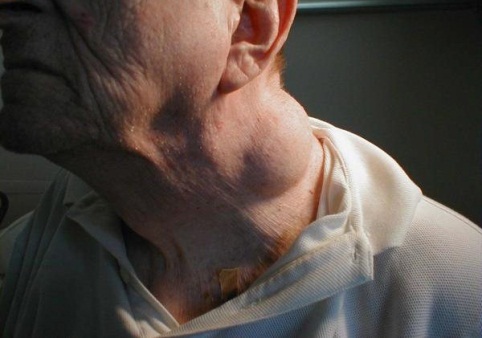
2. Puffy neck and pain in the throat. As the tumors grow and develop, they will start to push on the existing structures of your throat. It is also common to experience swelling, which can lead to further discomfort. Pressure may develop in your nose and ears due to the excessive growth. If you notice a significant amount of growth or puffiness in the neck, this could be a sign that you are developing throat cancer. It is especially serious if the swelling is interrupting your ability to eat and/or breathe normally.
Make special note of whether or not your lymph nodes are swollen. These glands tend to absorb toxins, which makes them incredibly susceptible to infections and cancers.
3. Coughing and changes in voice. If you are developing cancer in the vocal chords or larynx, coughing is a common side effect. You may feel as though something is caught in your throat or show symptoms similar to those associated with streptococcus. Your throat may constantly feel raw and irritated, and you may notice a significant increase in your mucus levels. The development of a cancerous sore near your vocal chords may also cause your voice to become hoarse and raspy.
4. Weight loss. If you have not been eating at your usual rate because your throat is sore, you may start losing weight. An issue arises if you are not eating less, but still appear to be dropping a significant amount of weight. This is a sign that your body may not be absorbing nutrients properly, which can be attributed to damaged cells in your esophagus or saliva glands. A tumor that is growing at a significant rate may also absorb nutrients faster than other cells, which can lead to weight loss throughout the rest of the body.
5. Other symptoms
Any of these symptoms can be the result of other diseases that are much less serious. If you are suffering from multiple symptoms, or the symptoms you have are not healing over time, then you must seek medical attention. Your doctor can perform x-rays, a physical examination, or a CT scan to determine if you have a cancerous growth. Your doctor may also perform a biopsy on a growth that has developed in your mouth or throat. This will determine whether or not it is cancerous. These results will also help determine the proper course of treatment.
Like all cancers, throat cancer develops when the cells in your throat begin developing genetic mutations. These cells will start to grow at an uncontrollable rate, killing off healthy cells and creating large, uncomfortable tumors. Unlike some other forms of the disease, it is not currently known what causes the mutation that leads to throat cancer. However, there are a few risk factors that are likely to lead to the development of this disease if they are not avoided.
1. Excessive substance use. The excessive use of tobacco or alcohol has been linked to the development of throat cancer. These substances irritate the throat and kill off healthy cells. They also dry out the throat, making it difficult for the body to create a healthy mucous membrane that protects the cells from harsh stimulants. This means that your throat will be more likely to develop cancer-related issues, as will your lungs and stomach. Harsh stimulants that would normally be expelled with your mucus will enter your system and cause damage throughout your body.
2. Poor diet. The best way to prevent cancer is to encourage healthy cell growth. Getting the right nutrients will help your body grow and develop properly. Some foods are also shown to help prevent cancer cells from developing. According to the American Cancer Society, a diet that does not include plenty of fruits, vegetables, vitamin C, and beta-carotene can lead to the development of throat cancer. Patients should also limit red meat intake and avoid foods that can lead to obesity. Both of these lead to excessive amounts of sugar and fat clinging to cells in the throat, which makes the patient more susceptible to mouth infections. A high number of mouth infections lowers the area's defenses, making you much more susceptible to cancer.
3. Poor hygiene or exposure to certain chemicals. For similar reasons, it is incredibly important to keep your mouth clean. The mouth is one of the dirtiest places in the human body. The moist conditions make it very easy for bacteria and viruses to grow, which can lead to serious infections. Harsh chemicals such as asbestos also make it difficult for your body to fight off infections in the throat. This will leave you susceptible to developing abnormal cells that could become cancerous