Where Is the Scaphoid Bone?
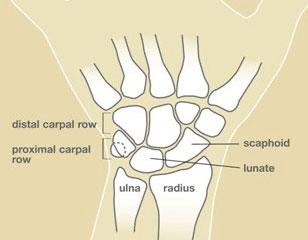 The hand contains a set of eight small bones which are referred to as the carpal bones. These bones are arranged in two rows with one row lying on the top of the other. The proximal row contains the triquetrum, scaphoid, pisiform and lunate bones, while the distal row which lies below it contains the trapezoid, hamate, trapezium and capitate bones. The row of bones that lies closest to the elbow is the proximal one.
The hand contains a set of eight small bones which are referred to as the carpal bones. These bones are arranged in two rows with one row lying on the top of the other. The proximal row contains the triquetrum, scaphoid, pisiform and lunate bones, while the distal row which lies below it contains the trapezoid, hamate, trapezium and capitate bones. The row of bones that lies closest to the elbow is the proximal one.
The scaphoid bone lies on the thumb side of the wrist and is one of the largest carpal bones. It resembles a cashew nut both in looks and size and does the job of linking and stabilizing the two rows of carpal bones. The radius and the wrist joint is where the lunate and scaphoid bones mesh with each other.
What Causes Scaphoid Fracture?
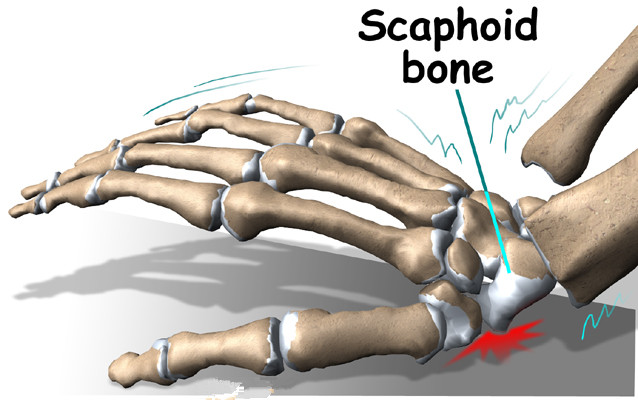 A scaphoid fracture is usually the result of compression of the scaphoid bone against any bone of the radius (the forearm). The most common reason for this fracture is direct contact of the palm with the ground, which is caused by instance falling on the hand while the arm is in an outstretched position. When you are falling on the ground, your wrist would be bent backwards and your palm will be stretched out and flat, which is usually an instinctive position you will take to protect yourself during a forward fall.
A scaphoid fracture is usually the result of compression of the scaphoid bone against any bone of the radius (the forearm). The most common reason for this fracture is direct contact of the palm with the ground, which is caused by instance falling on the hand while the arm is in an outstretched position. When you are falling on the ground, your wrist would be bent backwards and your palm will be stretched out and flat, which is usually an instinctive position you will take to protect yourself during a forward fall.
What Are the Symptoms of Scaphoid Fracture?
The telltale signs of a scaphoid fracture are:
- pain felt on the thumb side of the wrist
- bruising and swelling at the base of the thumb
- inability to grip objects firmly
If the pain and discomfort that you are feeling in your wrist after an injury last for more than a day, it is a sign that a fracture has occurred. If the pain does not go away, then it becomes necessary that you seek medical care as there is little chance that the pain would be caused due to a sprained wrist.
If you suspect that your scaphoid bone is fractured, refer to the video below to determine it.
How Is Scaphoid Fracture Treated?
1. Nonsurgical Treatment
- Fracture. Wearing a cast for up to 12 weeks is the usual treatment for a fracture that is in good alignment and has been diagnosed shortly. The forearm, wrist and thumb would be covered by the cast which will keep the scaphoid bone still so that it can heal properly. X-rays taken each month can help your doctor in keeping an eye on the healing progress. The cast will be removed once the fracture has healed; however, there still remains a chance for non-union.
- Nonunion. Fractures that don’t heal within four months are called non-unions. In such cases, wearing the cast for an extended period is recommended if the injury is a recent one. An electrical stimulator, a device which sends small amounts of electric current to the scaphoid bone and helps in healing it, is also prescribed by doctors and has to be worn like a bracelet for at least 10-12 hours each day.
2. Surgery
- Screw Fixation. In cases of non-displaced scaphoid fractures, a surgery, such as screw fixation, can prove to be very effective. In this surgery, a screw is inserted through the scaphoid and it holds the scaphoid bone firmly while it heals. Studies have revealed that that it can help you in returning to your daily routine much quickly than wearing a cast.
- Scaphoid Debridement. Non-unions that occur after using an electrical stimulator or wearing a cast have to be treated with surgical procedure known as scaphoid debridement. This surgery involves making an incision in the wrist over the scaphoid bone and removing the scar tissue present on the bone. This allows healing to begin on the fresh bone surface.
- Bone Graft Method. A bone graft can also be used for surgical treatment of scaphoid fractures. A bone graft is a bone tissue taken from other wrist bones which is then inserted into the fracture. Bone grafts are taken either from the wrist or from the pelvis and can hasten the healing process on the bone’s surface.
What Are the Complications of Scaphoid Fracture?
If medical treatment is received at an early stage, the scaphoid fracture will not take much time to heal. However, if not, complications can arise which might include the following.
1. Delayed Union or Non-Union
Incomplete healing of the scaphoid bone even after being treated in a cast for four months means the occurrence of delayed union. If the fracture isn’t repaired at all and the bony fragments remain separated from each other, it is a sign of a non-union. Both these complications can occur if the fracture hadn’t been treated quickly enough. This is why it is important that a fractured wrist should be treated as quickly as possible. Positioning of the fracture, its displacement and involvement of avascular necrosis can all have an effect on the healing of a scaphoid fracture. Wearing a cast for an extended time period and surgery are the treatment options that are available to you in case a delayed or non-union occurs.
2. Malunion
Malunion occurs if the fragments of the scaphoid bone heal in an incorrect angle and not in their correct positions. In this case, you will find it difficult to grip and hold objects and suffer pain in moving the wrist. Scans or x-rays of the scaphoid bone can reveal the malunion and surgical intervention is necessary for correcting it.
3. Avascular Necrosis
Avascular necrosis is life threatening because of no blood supply. In most cases of scaphoid fracture, the waist which is the narrowest part of the scaphoid gets fractured. Since it is the entry point of blood supply to the scaphoid bone, a fracture here can impede the blood supply to a portion of the scaphoid bone. Thus, the scaphoid bone won’t be able to heal and a portion of it might die and breakup. X-ray of the scaphoid bone can reveal occurrence of avascular necrosis if done after a few months of the initial injury.
4. Arthritis
Some people might develop osteoarthritis after a fracture of the scaphoid bone. The chances of this happening increase if the complications of avascular necrosis, malunion or non-union have occurred.


