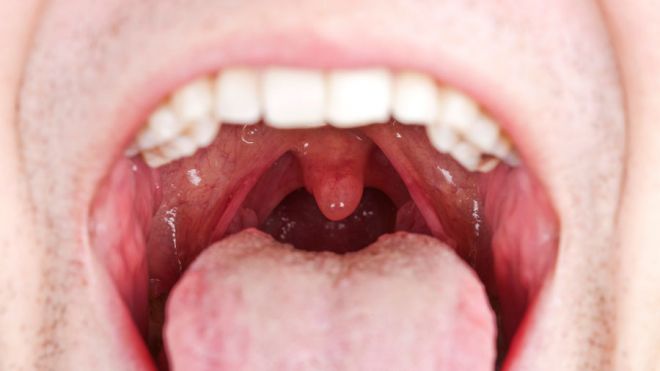
 The pharynx (upper portion of the throat) and mouth (oral cavity) are important for many functions such as swallowing, chewing and breathing. These are sometimes together referred to as the oral cavity or oropharynx, which includes the following important structures:
The pharynx (upper portion of the throat) and mouth (oral cavity) are important for many functions such as swallowing, chewing and breathing. These are sometimes together referred to as the oral cavity or oropharynx, which includes the following important structures:
- Salivary glands
- Area behind your wisdom teeth
- Roof of your mouth (both the hard and soft palate)
- Floor of your mouth
- Tongue
- Gums
- Teeth
- Inner lining of your cheeks
- Lips
These structures are made up of many different types of cells. Mouth and throat cancer develops if the normal cells transform and grow multiply without the normal controls.
Causes of Mouth and Throat Cancer
1. Smoking
Every form of smoking, like cigarettes, pipes and cigars, has been linked to mouth and throat cancer. It may also cause cancer in other organs, including the bladder and lungs. Chewing or smokeless tobacco can cause cancer on the inner lips, cheeks and gums.
2. Alcohol
At least 75% of those with mouth and throat cancer drink alcohol frequently and alcoholwill increase the risk six times of developing one of those types of cancer.
3. Sun Exposure
The sun’s UV radiation can also increase your risk of lip cancer. Those who work outdoors or spend more time outside have an increased risk of lip cancer.
4. HPV
Some strains of HPV (human papillomavirus) have been linked to cancer of the vulva, vagina, cervix and penis. Certain types may also infect mouth and throat tissues. It is also associated with cancer of the soft palate, tonsils, back of a person’s throat and tongue base.
Symptoms of Mouth and Throat Cancer
1. Symptoms of Mouth Cancer
Mouth cancer symptoms may include the following:
- Feeling as if something is stuck in the throat
- Sore throat
- Pain or difficulty chewing or swallowing
- Jaw stiffness or pain
- Tongue pain
- Dentures that fit poorly
- Loose teeth
- A reddish or white patch on the inner mouth
- A thickening of the mouth lining, skin or a lump there
- A sore which won’t heal
You can see the video to understand mouth cancer in detail:
2. Symptoms of Throat Cancer
The following symptoms may indicate the presence of throat cancer:
- Weight loss
- A sore throat
- A sore or lump which won’t heal
- Ear pain
- Trouble swallowing
- Hoarseness or other changes in voice
- A cough
You can see the videos to understand throat cancer in detail:
When to See a Doctor
You should make an appointment with your doctor when you notice persistent symptoms or signs which bother you or last over two weeks.
Treatments of Mouth and Throat Cancer
1. Surgery
In the case of mouth cancer, there are three main options for surgery. Surgery to remove the tumor would involve cutting out the tumor as well as the healthy surrounding tissues. In cases where the cancer cells are in the neck’s lymph nodes, your surgeon might recommend removing these cancerous tissues as well as related tissues within the neck. In some cases, your doctor might suggestion reconstructive surgery for functional reasons, such as ease of eating and talking, or aesthetic ones.
The surgical options for throat cancer are similar, but it generally depend on the spread of the cancer. In the case of early stage cancer, an endoscopy may be enough and this procedure would remove minor cancers from the vocal cords or throat surface. If the tumors have reached the voice box, your doctor will usually attempt to leave some of the unaffected area, but it may be necessary to remove the entire voice box in some cases (laryngectomy). Removing all or some of the throat (a pharyngectomy) may also be necessary.
2. Radiation Therapy
Radiation relies on high energy beams which kill the cancer cells via radiation. It can be external with a large machine or internal with small radioactive wires and seeds. Sometimes no further treatment is necessary in the case of early-stage cancers, but in the case of advanced cancers, it might be combined with surgery or chemotherapy. It can also be used to help relieve pain and other symptoms.
3. Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy uses chemicals in order to kill the cancer cells and may be done alone or combined with other treatments. It is frequently combined with radiation therapy as it can increase the effectiveness. The side effects will depend on the drug used, which can include hair loss, vomiting and nausea.
4. Targeted Drug Therapy
This therapy uses the defects of cancer cells against them. One example for throat or mouth cancer is Cetuximab (Erbitux) which can stop an important protein from acting effectively. Researchers are conducting clinical trials to test other drugs. These are typically combined with radiation or chemotherapy.
Preventions of Mouth and Throat Cancer
The following preventative measures are based on the various causes of throat and mouth cancer.
- Avoid Irritation. Avoid any causes of oral irritation such as dentures that fit poorly. If you wear dentures, have them checked regularly and clean them daily.
- Avoid Sun Exposure. Always wear protective clothing when exposed to the UV rays of the sun. Apply sunscreen on the face and use a lip balm containing it. Also wear a hat with a wide brim.
- Don't Smoke. If you do smoke, quit as soon as possible. Remember that other methods of consuming tobacco do not reduce the risk.
- Have a Balanced Diet. You should consume a balanced diet to avoid nutritional deficiencies. In particular, pay attention to dairy products, fruits, vegetables and other foods containing vitamin A. Don’t rely on supplements for vitamin A which can be harmful.
- Limit Alcohol. Only drink alcohol in moderation and never drink when you smoke tobacco.
- Protect yourself from HPV. To reduce your risk of developing HPV, limit your sexual partners and always use a condom.


